One instance of Postgres is known as a cluster .one cluster is on the disk known as a data directory
by default is located on “/var/lib/psql/11/data/”, this is the default location for the data directory
1. Global
-It contains cluster-wide database objects. we some files here each files some kind of tables or user info or metadata files which is related to the dictionary files or tables which pg_filenode.map = A file that maps internal relations (mainly system catalogue tables) to their OIDr here proper node file mapping info stored over here.
-It is an internal file that is used by the server when the server is started.
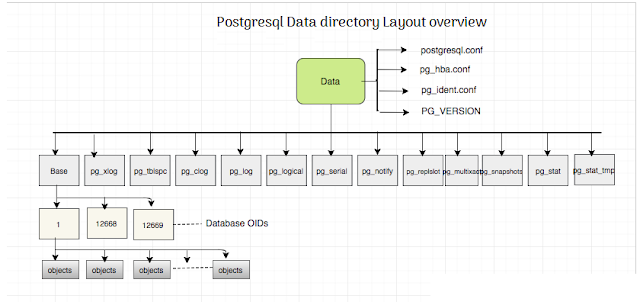
PostgreSQL Data directory Layout
2. Base
-It is the main directory and contains DB, inside the directory, we can see dB directories and its one directory per DB
3.pg_tblsc
-This is a directory that contains symbolic links to the tablespace locations, in case we have created the tablespace in our instance. Then link to the physical location of the tablespace It will be recreated inside the pg_tblsc directory
-We can see the links in case we have created the tablespaces.in case we used the default tablespace instead of creating new user tablespaces, we can’t see any links inside the directories
4.pg_wal
-It contains transaction logs or wal segments
-These files are binary-files
5.pg_log
-Which contains our start-up logs
6.logs
-Which contains the error log, All the error logs are located under these directories
-It is a human-readable file which is in text formats
7.Status Directories
-These are the multiple directories that start with pg_*, a lot of status data and lots of transaction info, temporary statistic info.
-It is just required the information of the server and content of the directories are temporary
8.Configuration Files
1.PostgreSQL.conf — one of the most parameter files inside the directory
2.pg_hba.conf — host-based access control file or host-based authentication file
3.pg_ident.conf — which is used for OS authentication
4.postgresql.auto.conf
5. postmaster. PID — which contains the postmaster details and is only available when the cluster is up and running
6.postmaster.opts — the option used to start the server
Comments
Post a Comment